
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic research
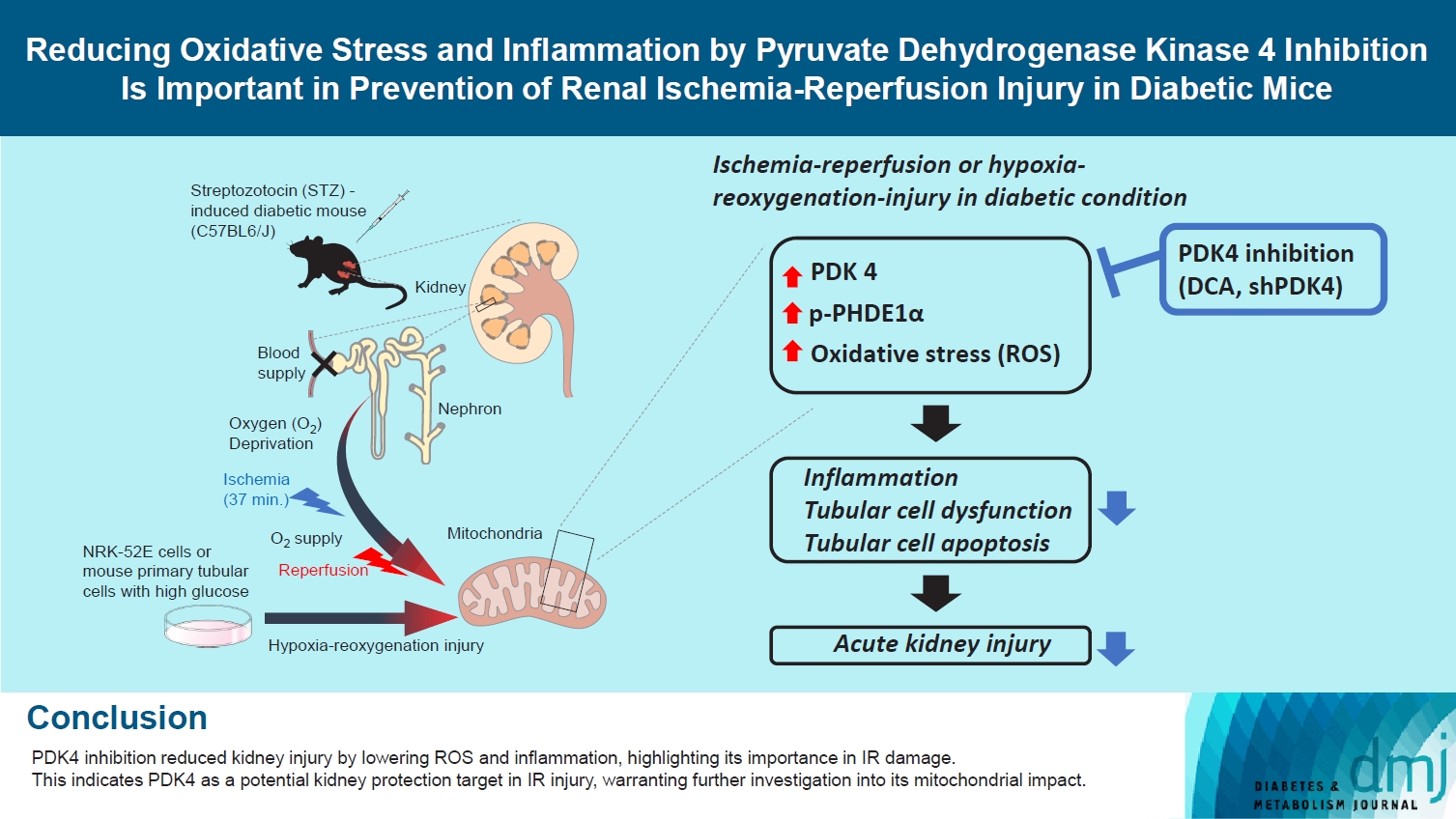
- Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 Inhibition Is Important in Prevention of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Mice
- Ah Reum Khang, Dong Hun Kim, Min-Ji Kim, Chang Joo Oh, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung Hee Choi, In-Kyu Lee
- Received June 22, 2023 Accepted July 13, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0196 [Epub ahead of print]
- 788 View
- 75 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammation are reported to have a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury, a leading cause of acute kidney injury. The present study investigated the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) in ROS production and inflammation following IR injury.
Methods
We used a streptozotocin-induced diabetic C57BL6/J mouse model, which was subjected to IR by clamping both renal pedicles. Cellular apoptosis and inflammatory markers were evaluated in NRK-52E cells and mouse primary tubular cells after hypoxia and reoxygenation using a hypoxia work station.
Results
Following IR injury in diabetic mice, the expression of PDK4, rather than the other PDK isoforms, was induced with a marked increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase E1α (PDHE1α) phosphorylation. This was accompanied by a pronounced ROS activation, as well as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) production. Notably, sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) attenuated renal IR injury-induced apoptosis which can be attributed to reducing PDK4 expression and PDHE1α phosphorylation levels. DCA or shPdk4 treatment reduced oxidative stress and decreased TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and MCP-1 production after IR or hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.
Conclusion
PDK4 inhibition alleviated renal injury with decreased ROS production and inflammation, supporting a critical role for PDK4 in IR mediated damage. This result indicates another potential target for reno-protection during IR injury; accordingly, the role of PDK4 inhibition needs to be comprehensively elucidated in terms of mitochondrial function during renal IR injury.
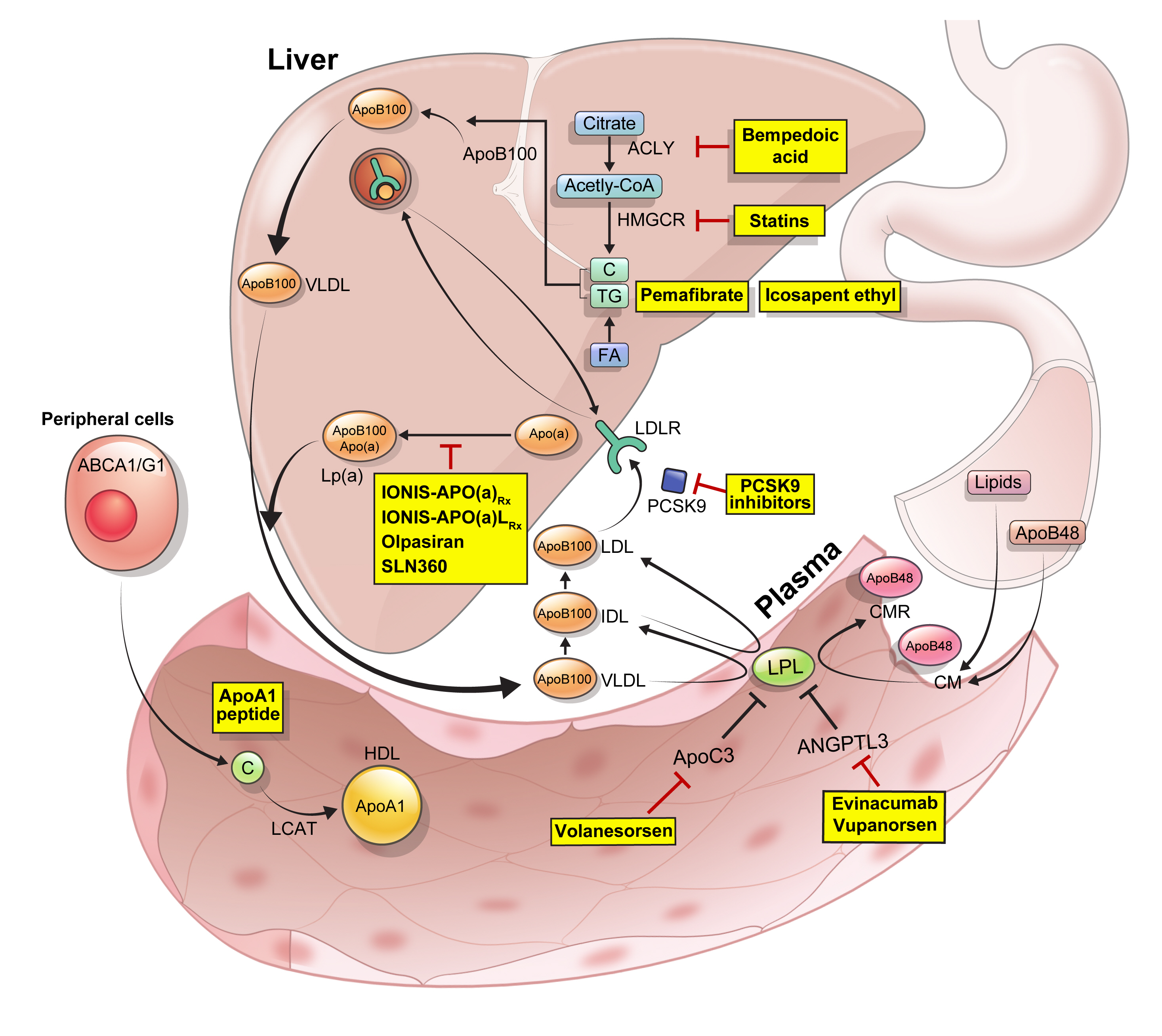
- New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
- Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):817-818. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0295
- Corrects: Diabetes Metab J 2022;46(4):517
- 2,064 View
- 144 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
- Drug/Regimen
- New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
- Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):517-532. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0198
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2022;46(5):817
- 9,946 View
- 864 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Statins are the cornerstone of the prevention and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). However, even under optimal statin therapy, a significant residual ASCVD risk remains. Therefore, there has been an unmet clinical need for novel lipid-lowering agents that can target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and other atherogenic particles. During the past decade, several drugs have been developed for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Inclisiran, a small interfering RNA that targets proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), shows comparable effects to that of PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies. Bempedoic acid, an ATP citrate lyase inhibitor, is a valuable treatment option for the patients with statin intolerance. Pemafibrate, the first selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator, showed a favorable benefit-risk balance in phase 2 trial, but the large clinical phase 3 trial (PROMINENT) was recently stopped for futility based on a late interim analysis. High dose icosapent ethyl, a modified eicosapentaenoic acid preparation, shows cardiovascular benefits. Evinacumab, an angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) monoclonal antibody, reduces plasma LDL-C levels in patients with refractory hypercholesterolemia. Novel antisense oligonucleotides targeting apolipoprotein C3 (apoC3), ANGPTL3, and lipoprotein(a) have significantly attenuated the levels of their target molecules with beneficial effects on associated dyslipidemias. Apolipoprotein A1 (apoA1) is considered as a potential treatment to exploit the athero-protective effects of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), but solid clinical evidence is necessary. In this review, we discuss the mode of action and clinical outcomes of these novel lipid-lowering agents beyond statins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of adherence in patients with chronic diseases
Michel Burnier
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 119: 1. CrossRef - Bempedoic acid: new evidence and recommendations on use
Kristina Paponja, Ivan Pećin, Željko Reiner, Maciej Banach
Current Opinion in Lipidology.2024; 35(1): 41. CrossRef - Genetic insights into repurposing statins for hyperthyroidism prevention: a drug-target Mendelian randomization study
Anqi Huang, Xinyi Wu, Jiaqi Lin, Chiju Wei, Wencan Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting host-specific metabolic pathways—opportunities and challenges for anti-infective therapy
Monika I. Konaklieva, Balbina J. Plotkin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) and Atherosclerosis: Does Hypolipidemic Treatment Have an Effect?
Petros Adamidis, Despoina Pantazi, Iraklis Moschonas, Evangelos Liberopoulos, Alexandros Tselepis
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2024; 11(3): 72. CrossRef - Modulating effects of crocin on lipids and lipoproteins: Mechanisms and potential benefits
Habib Yaribeygi, Mina Maleki, Farin Rashid-Farrokhi, Payman Raise Abdullahi, Mohammad Amin Hemmati, Tannaz Jamialahmadi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28837. CrossRef - Assessing the Benefits of Lifestyle Influences on Cardiovascu-lar Health After Acute Coronary Syndrome
Marius Rus, Claudia Elena Stanis, Paula Marian, Lilliana Oana Pobirci, Loredana Ioana Banszki, Veronica Huplea, Gheorghe Adrian Osiceanu, Bianca-Maria Pop, Gabriela Dogaru, Felicia Liana Andronie-Cioara
Balneo and PRM Research Journal.2024; 15(Vol.15, no): 660. CrossRef - Liver cancer cells as the model for developing liver-targeted RNAi therapeutics
Beibei Hou, Linhui Qin, Linfeng Huang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2023; 644: 85. CrossRef - Insights into Causal Cardiovascular Risk Factors from Mendelian Randomization
C. M. Schooling, J. V. Zhao
Current Cardiology Reports.2023; 25(2): 67. CrossRef - Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside and anethole ameliorate lipid abnormalities, oxidative injury, hypercholesterolemia, heart, and liver conditions
Sana Noreen, Habib‐ur Rehman, Tabussam Tufail, Huma Badar Ul Ain, Chinaza Godswill Awuchi
Food Science & Nutrition.2023; 11(6): 2620. CrossRef - Colesterol remanente, riesgo vascular y prevención de la arteriosclerosis
Xavier Pintó, Marta Fanlo, Virginia Esteve, Jesús Millán, Agustín Blanco, Mariano Blasco, José Luís Díaz Díaz, Ángel Díaz Rodríguez, Alipio Mangas, Vicente Pascual, Juan Pedro Botet, Pablo Pérez Martínez
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis.2023; 35(4): 206. CrossRef - Evolving Management of Low‐Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: A Personalized Approach to Preventing Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Across the Risk Continuum
Michael J. Wilkinson, Norman E. Lepor, Erin D. Michos
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The cell origins of foam cell and lipid metabolism regulated by mechanical stress in atherosclerosis
Zhi Ouyang, Jian Zhong, Junyi Shen, Ye Zeng
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Metabolism: Key Regulators of Their Flux
Alejandro Gugliucci
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4399. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol, vascular risk, and prevention of atherosclerosis
Xavier Pintó, Marta Fanlo, Virginia Esteve, Jesús Millán
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis (English Edition).2023; 35(4): 206. CrossRef - Antibiotics and Lipid-Modifying Agents: Potential Drug–Drug Interactions and Their Clinical Implications
Marios Spanakis, Danny Alon-Ellenbogen, Petros Ioannou, Nikolaos Spernovasilis
Pharmacy.2023; 11(4): 130. CrossRef - Advances in Treatment of Dyslipidemia
Jill Dybiec, Wiktoria Baran, Bartłomiej Dąbek, Piotr Fularski, Ewelina Młynarska, Ewa Radzioch, Jacek Rysz, Beata Franczyk
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13288. CrossRef - Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Lipoprotein Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Elena Valeria Fuior, Evangelia Zvintzou, Theodosios Filippatos, Katerina Giannatou, Victoria Mparnia, Maya Simionescu, Anca Violeta Gafencu, Kyriakos E. Kypreos
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2696. CrossRef - Preparation, characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study of ginsenoside Rb1-PLGA nanoparticles
Lixin Du, Huiling Lu, Yifei Xiao, Zhihua Guo, Ya Li
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dysregulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis in Ovarian Cancer
Zahraa Qusairy, Anne Gangloff, Shuk On Annie Leung
Current Oncology.2023; 30(9): 8386. CrossRef - Riesgo residual. Conclusiones
Ángel Cequier, José Luis Zamorano
Revista Española de Cardiología Suplementos.2023; 23: 25. CrossRef - Causal effects of circulating lipids and lipid-lowering drugs on the risk of urinary stones: a Mendelian randomization study
Zilong Tan, Jing Hong, Aochuan Sun, Mengdi Ding, Jianwu Shen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of residual cardiovascular risk: trends and frontiers
Lin Wang, Sutong Wang, Chaoyuan Song, Yiding Yu, Yuehua Jiang, Yongcheng Wang, Xiao Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Understanding on the Genetic Basis of Key Metabolic Disorders: A Review
Kenneth Francis Rodrigues, Wilson Thau Lym Yong, Md. Safiul Alam Bhuiyan, Shafiquzzaman Siddiquee, Muhammad Dawood Shah, Balu Alagar Venmathi Maran
Biology.2022; 11(9): 1308. CrossRef - Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 575. CrossRef
- The role of adherence in patients with chronic diseases
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Higher Muscle Mass Protects Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus from Progression to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yujin Shin, Joon Ho Moon, Tae Jung Oh, Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):890-900. Published online April 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0334
- 4,755 View
- 228 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated whether postpartum muscle mass affects the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Korean women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Methods
A total of 305 women with GDM (mean age, 34.9 years) was prospectively evaluated for incident prediabetes and T2DM from 2 months after delivery and annually thereafter. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) was assessed with bioelectrical impedance analysis at the initial postpartum visit, and ASM, either divided by body mass index (BMI) or squared height, and the absolute ASM were used as muscle mass indices. The risk of incident prediabetes and T2DM was assessed according to tertiles of these indices using a logistic regression model.
Results
After a mean follow-up duration of 3.3 years, the highest ASM/BMI tertile group had a 61% lower risk of incident prediabetes and T2DM compared to the lowest tertile group, and this remained significant after we adjusted for covariates (adjusted odds ratio, 0.37; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15 to 0.92; P=0.032). Equivalent findings were observed in normal weight women (BMI <23 kg/m2), but this association was not significant for overweight women (BMI ≥23 kg/m2). Absolute ASM or ASM/height2 was not associated with the risk of postpartum T2DM.
Conclusion
A higher muscle mass, as defined by the ASM/BMI index, was associated with a lower risk of postpartum prediabetes and T2DM in Korean women with GDM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- More appendicular lean mass relative to body mass index is associated with lower incident diabetes in middle-aged adults in the CARDIA study
Melanie S. Haines, Aaron Leong, Bianca C. Porneala, Victor W. Zhong, Cora E. Lewis, Pamela J. Schreiner, Karen K. Miller, James B. Meigs, Mercedes R. Carnethon
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(1): 105. CrossRef - The Association of the Triglyceride and Muscle to Fat Ratio During Early Pregnancy with the Development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Fang Wang, Yuan-Yuan Bao, Kang Yu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3187. CrossRef - Correlation of body composition in early pregnancy on gestational diabetes mellitus under different body weights before pregnancy
Li Xintong, Xu Dongmei, Zhang Li, Cao Ruimin, Hao Yide, Cui Lingling, Chen Tingting, Guo Yingying, Li Jiaxin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- More appendicular lean mass relative to body mass index is associated with lower incident diabetes in middle-aged adults in the CARDIA study
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Efficacy of Glimepiride, Alogliptin, and Alogliptin-Pioglitazone as the Initial Periods of Therapy in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study
- Hae Jin Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Kyu Yeon Hur, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Sung Wan Chun, Eun Seok Kang, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):689-700. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0183
- 5,656 View
- 377 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The choice of an optimal oral hypoglycemic agent in the initial treatment periods for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients remains difficult and deliberate. We compared the efficacy and safety of glimepiride (GLIM), alogliptin (ALO), and alogliptin-pioglitazone (ALO-PIO) in poorly controlled T2DM patients with drug-naïve or metformin failure.
Methods
In this three-arm, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled trial, poorly controlled T2DM patients were randomized to receive GLIM (n=35), ALO (n=31), or ALO-PIO (n=33) therapy for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was change in the mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels at week 24 from baseline. Secondary endpoints were changes in HbA1c level at week 12 from baseline, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, lipid profiles at weeks 12 and 24, and parameters of glycemic variability, assessed by continuous glucose monitoring for 24 weeks.
Results
At weeks 12 and 24, the ALO-PIO group showed significant reduction in HbA1c levels compared to the ALO group (–0.96%±0.17% vs. –0.37%±0.17% at week 12; –1.13%±0.19% vs. –0.18%±0.2% at week 24). The ALO-PIO therapy caused greater reduction in FPG levels and significant increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels at weeks 12 and 24 than the ALO therapy. Compared to low-dose GLIM therapy, ALO-PIO therapy showed greater improvement in glycemic variability. The adverse events were similar among the three arms.
Conclusion
ALO-PIO combination therapy during the early period exerts better glycemic control than ALO monotherapy and excellency in glycemic variability than low-dose sulfonylurea therapy in uncontrolled, drug-naïve or metformin failed T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
Fatma Haddad, Ghadeer Dokmak, Maryam Bader, Rafik Karaman
Life.2023; 13(4): 1012. CrossRef - Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Antidiabetic Treatment
Ruili Yin, Yongsong Xu, Xin Wang, Longyan Yang, Dong Zhao
Molecules.2022; 27(10): 3055. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
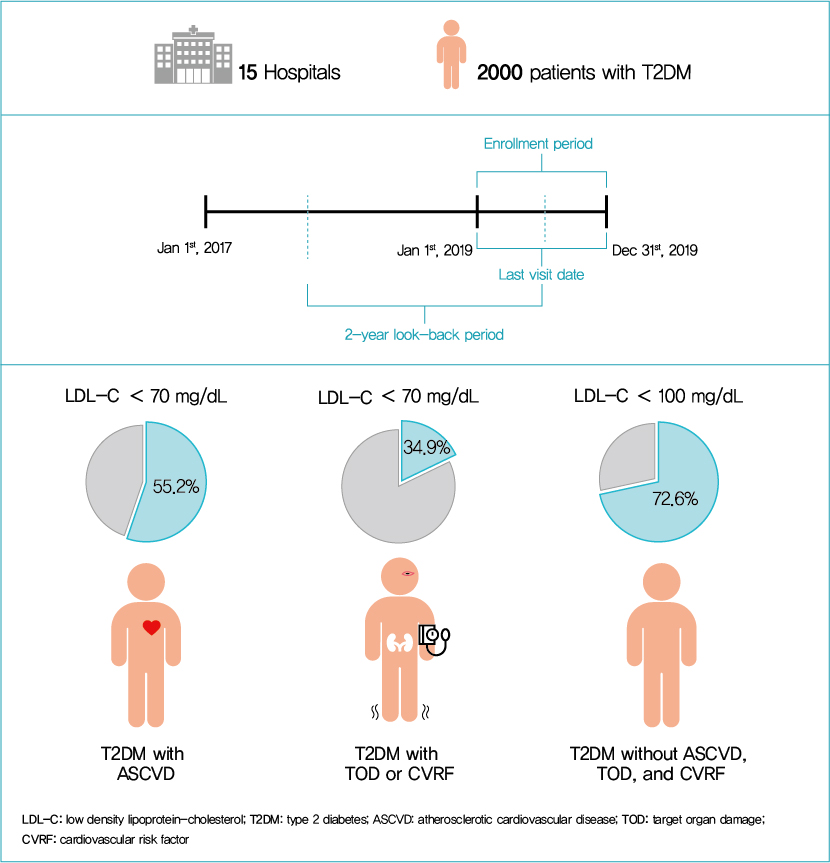
- Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
- Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. Published online March 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
- 6,938 View
- 347 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Distinct effects of rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe on senescence markers of CD8+ T cells in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Joung Youl Lim, Minchul Song, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Technology/Device
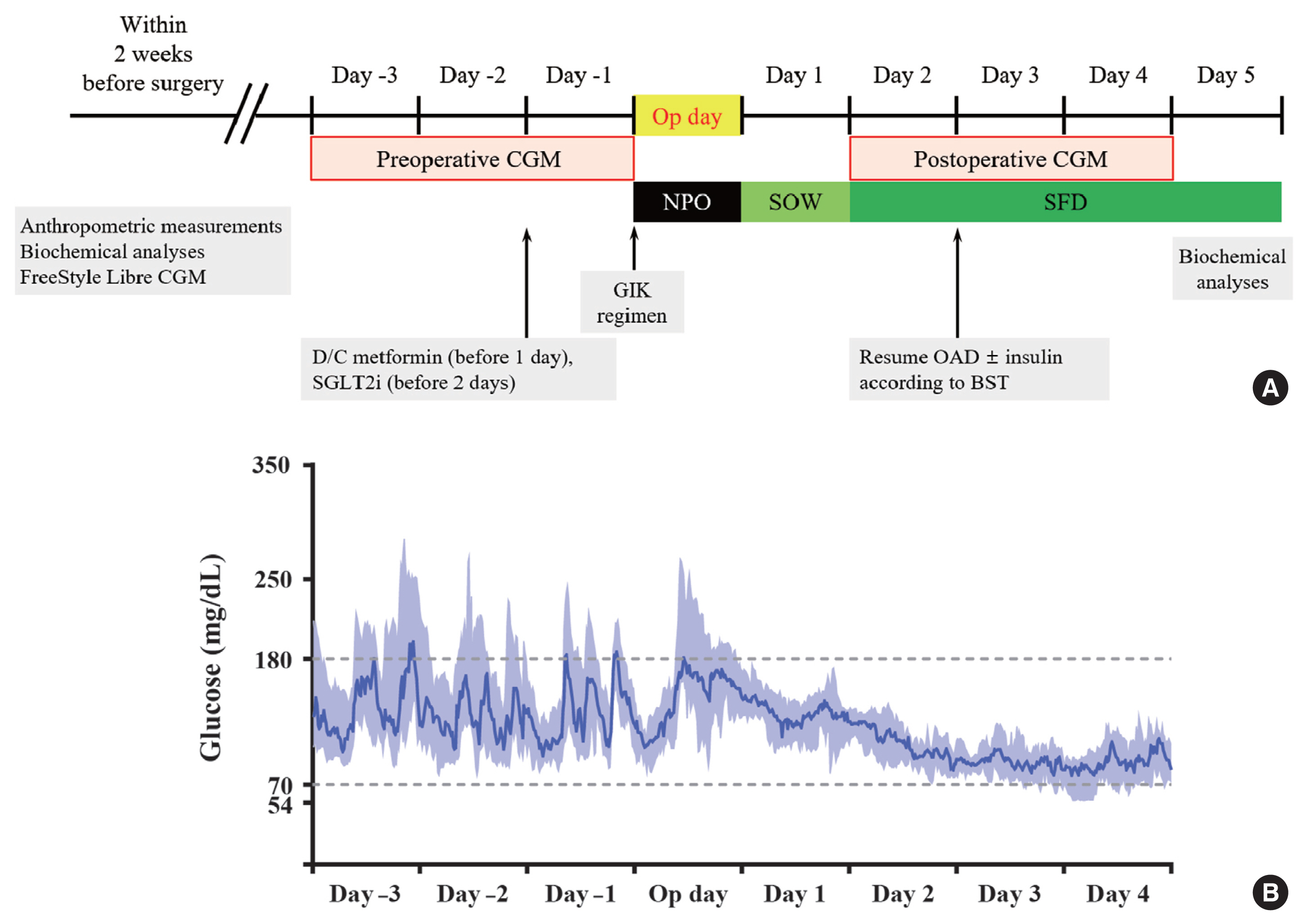
- Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
- Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):713-721. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0164
- 4,791 View
- 317 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been widely used in the management of diabetes. However, the usefulness and detailed data during perioperative status were not well studied. In this study, we described the immediate changes of glucose profiles after metabolic surgery using intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This was a prospective, single-center, single-arm study including 20 participants with T2DM. The isCGM (FreeStyle Libre CGM) implantation was performed within 2 weeks before surgery. We compared CGM metrics of 3 days before surgery and 3 days after surgery, and performed the correlation analyses with clinical variables.
Results
The mean glucose significantly decreased after surgery (147.0±40.4 to 95.5±17.1 mg/dL, P<0.001). Time in range (TIR; 70 to 180 mg/dL) did not significantly change after surgery in total. However, it was significantly increased in a subgroup of individuals with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥8.0%. Time above range (>250 or 180 mg/dL) was significantly decreased in total. In contrast, time below range (<70 or 54 mg/dL) was significantly increased in total and especially in a subgroup of individuals with HbA1c <8.0% after surgery. The coefficient of variation significantly decreased after surgery. Higher baseline HbA1c was correlated with greater improvement in TIR (rho=0.607, P=0.005).
Conclusion
The isCGM identified improvement of mean glucose and glycemic variability, and increase of hypoglycemia after metabolic surgery, but TIR was not significantly changed after surgery. We detected an increase of TIR only in individuals with HbA1c ≥8.0%. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Ji Soo Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Kyung-Il Park, Seung-Won Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 312. CrossRef - Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients Following Bariatric Surgery: A Scoping Review
Yang Yu, Susan W. Groth
Obesity Surgery.2023; 33(8): 2573. CrossRef - Asymptomatic Hypoglycemia after Metabolic Surgery: New Insights from Perioperative Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Sang-Man Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 675. CrossRef
- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Complications
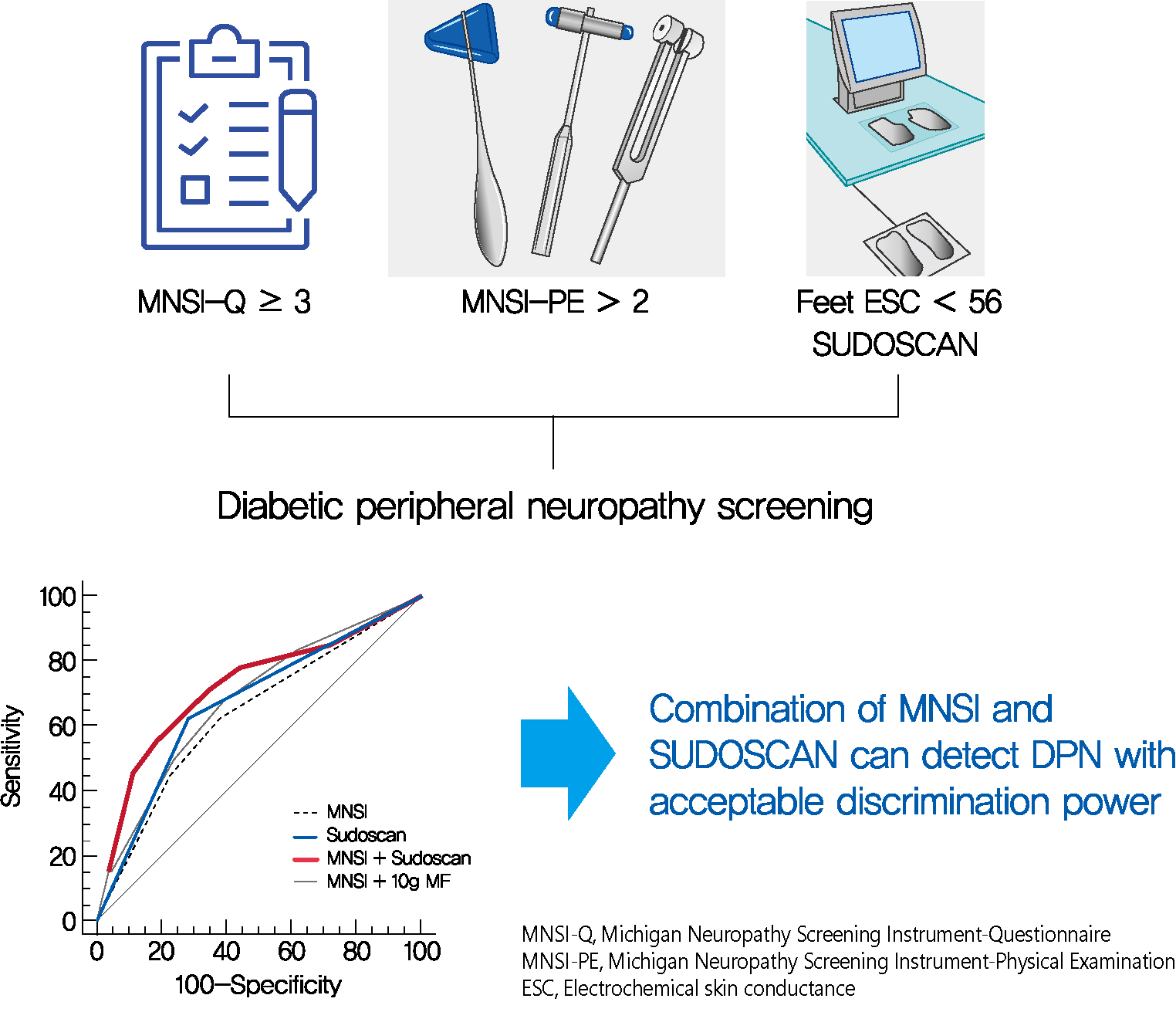
- SUDOSCAN in Combination with the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Is an Effective Tool for Screening Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):319-326. Published online September 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0014
- 5,823 View
- 314 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is important to prevent severe foot complication, but the detection rate of DPN is unsatisfactory. We investigated whether SUDOSCAN combined with Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) could be an effective tool for screening for DPN in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in clinical practice.
Methods
We analysed the data for 144 people with T2DM without other cause of neuropathy. The presence of DPN was confirmed according to the Toronto Consensus criteria. Electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) of the feet was assessed using SUDOSCAN. We compared the discrimination power of following methods, MNSI only vs. SUDOSCAN only vs. MNSI plus SUDOSCAN vs. MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test.
Results
Confirmed DPN was detected in 27.8% of the participants. The optimal cut-off value of feet ESC to distinguish DPN was 56 μS. We made the DPN screening scores using the corresponding odds ratios for MNSI-Questionnaire, MNSI-Physical Examination, SUDOSCAN, and 10-g monofilament test. For distinguishing the presence of DPN, the MNSI plus SUDOSCAN model showed higher areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) than MNSI only model (0.717 vs. 0.638, P=0.011), and SUDOSCAN only model or MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test showed comparable AUC with MNSI only model.
Conclusion
The screening model for DPN that includes both MNSI and SUDOSCAN can detect DPN with acceptable discrimination power and it may be useful in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ming Wang, Niuniu Chen, Yaxin Wang, Jiaying Ni, Jingyi Lu, Weijing Zhao, Yating Cui, Ronghui Du, Wei Zhu, Jian Zhou
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients by predominantly increasing large-fiber lesions
Sijia Fei, Jingwen Fan, Jiaming Cao, Huan Chen, Xiaoxia Wang, Qi Pan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111585. CrossRef - Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options
Raffaele Galiero, Alfredo Caturano, Erica Vetrano, Domenico Beccia, Chiara Brin, Maria Alfano, Jessica Di Salvo, Raffaella Epifani, Alessia Piacevole, Giuseppina Tagliaferri, Maria Rocco, Ilaria Iadicicco, Giovanni Docimo, Luca Rinaldi, Celestino Sardu, T
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3554. CrossRef - Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in resource-limited settings
Ken Munene Nkonge, Dennis Karani Nkonge, Teresa Njeri Nkonge
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of electrochemical skin conductance measurement by Sudoscan® for assessing autonomic dysfunction in peripheral neuropathies beyond diabetes
Jean-Pascal Lefaucheur
Neurophysiologie Clinique.2023; 53(2): 102859. CrossRef - Electrochemical skin conductances values and clinical factors affecting sudomotor dysfunction in patients with prediabetes, type 1 diabetes, and type 2 diabetes: A single center experience
Bedia Fulya Calikoglu, Selda Celik, Cemile Idiz, Elif Bagdemir, Halim Issever, Jean-Henri Calvet, Ilhan Satman
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 499. CrossRef - Autonomic Nerve Function Tests in Patients with Diabetes
Heung Yong Jin, Tae Sun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 71. CrossRef - Validation of the Body Scan®, a new device to detect small fiber neuropathy by assessment of the sudomotor function: agreement with the Sudoscan®
Jean-Pierre Riveline, Roberto Mallone, Clarisse Tiercelin, Fetta Yaker, Laure Alexandre-Heymann, Lysa Khelifaoui, Florence Travert, Claire Fertichon, Jean-Baptiste Julla, Tiphaine Vidal-Trecan, Louis Potier, Jean-Francois Gautier, Etienne Larger, Jean-Pas
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Electrochemical Skin Conductance by Sudoscan in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Liang-Te Chiu, Yu-Li Lin, Chih-Hsien Wang, Chii-Min Hwu, Hung-Hsiang Liou, Bang-Gee Hsu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 187. CrossRef - The Presence of Clonal Hematopoiesis Is Negatively Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Han Song, Youngil Koh, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 243. CrossRef - Case report: Significant relief of linezolid-induced peripheral neuropathy in a pre-XDR-TB case after acupuncture treatment
Yuping Mo, Zhu Zhu, Jie Tan, Zhilin Liang, Jiahui Wu, Xingcheng Chen, Ming Hu, Peize Zhang, Guofang Deng, Liang Fu
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of sudomotor alterations evaluated by Sudoscan in patients with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Ana Cristina García-Ulloa, Paloma Almeda-Valdes, Teresa Enedina Cuatecontzi-Xochitiotzi, Jorge Alberto Ramírez-García, Michelle Díaz-Pineda, Fernanda Garnica-Carrillo, Alejandra González-Duarte, K M Venkat Narayan, Carlos Alberto Aguilar-Salinas, Sergio H
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(6): e003005. CrossRef
- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
- COVID-19
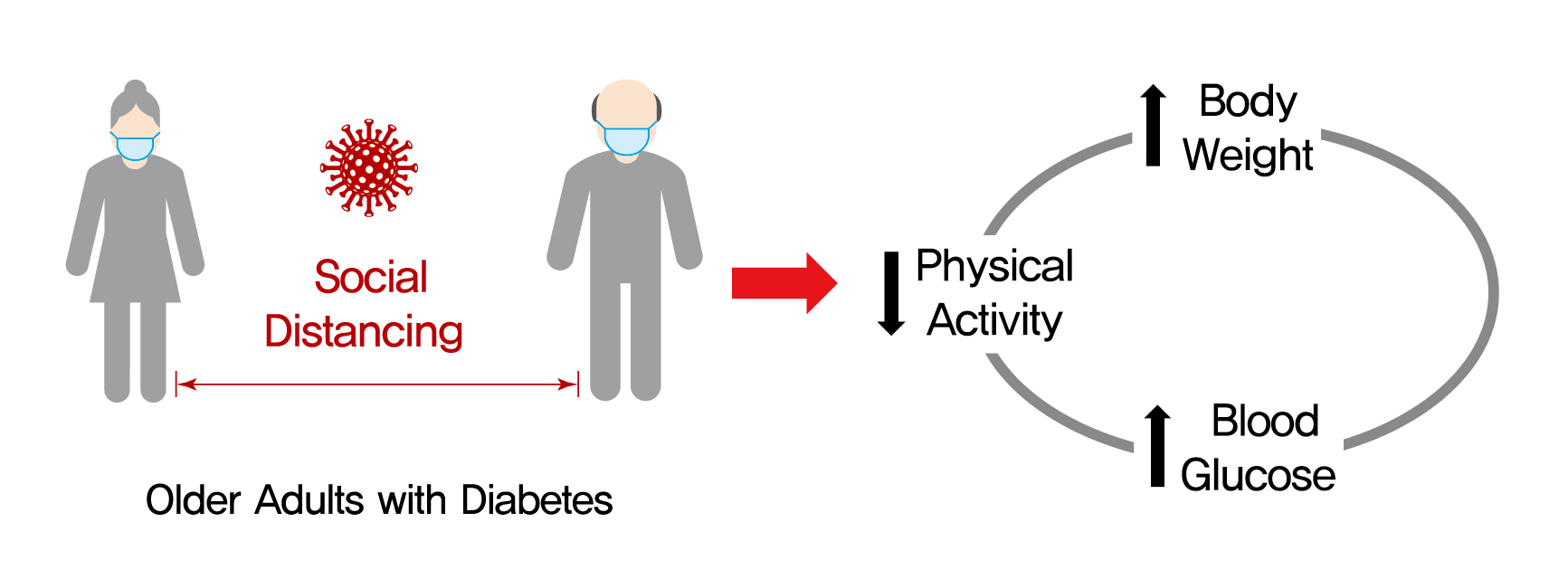
- Effects of Social Distancing on Diabetes Management in Older Adults during COVID-19 Pandemic
- Soo Myoung Shin, Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):765-772. Published online August 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0096
- 5,960 View
- 191 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
On March 22, 2020, intense social distancing (SD) was implemented in Korea to prevent the spread of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19). This study examined the impact of SD on diabetes control in older adults with diabetes.
Methods
Adults aged 60 to 90 years with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were physically and mentally independent were recruited. Participants who had complete blood chemistry data from April to July 2019 (pre-SD era) and April to July 2020 (SD era) were enrolled. Data were obtained about physical activity, nutrition, sarcopenia, and psychological and mental health from questionnaires in April to July 2020. Calf circumference was measured.
Results
In total, 246 people (100 men, 146 women; mean age, 73.8±5.7 years) participated in this study. The levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c, 7.4%±1.0% vs. 7.1%±0.8%, P<0.001), fasting glucose (142.2±16.7 mg/dL vs. 132.0±27.7 mg/dL, P<0.001), and body weight (62.6±9.4 kg vs. 61.8±10.1 kg, P<0.01) were higher in the SD era than in the pre-SD era. Total physical activity was lower in the SD era (2,584.6±2,624.1 MET-min/week–1 vs. 1,987.3±2,295.0 MET-min/week–1, P<0.001). A larger increase in HbA1c level was associated with increased body weight and decreased physical activity.
Conclusion
SD had negative effects on diabetes management in older adults with diabetes. Fasting glucose and HbA1c levels and body weight increased during the SD era. Participants with reduced physical activity gained more weight and had higher blood glucose levels. Given that the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, health professionals and diabetes educators should monitor changes in lifestyle factors in older adults with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preliminary efficacy of a technology-based physical activity intervention for older Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
Soonhyung Kwon, Oejin Shin, Rosalba Hernandez
Educational Gerontology.2024; 50(1): 27. CrossRef - Obesity and weight change during the COVID‐19 pandemic in children and adults: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Laura N. Anderson, Yulika Yoshida‐Montezuma, Nora Dewart, Ezza Jalil, Jayati Khattar, Vanessa De Rubeis, Sarah Carsley, Lauren E. Griffith, Lawrence Mbuagbaw
Obesity Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in lifestyle-related behaviour during the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan: a questionnaire survey for examinees who underwent an annual health check-up
Miyako Kishimoto, Kayo Masuko, Sumie Yamamoto, Retsu Fujita, Shoko Nakamura, Masato Odawara, Mikio Zeniya
Journal of International Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycaemic monitoring and control among high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes in Australian general practice during COVID-19
Kirrilee Jane Barlow, Paul P Fahey, Evan Atlantis
Family Medicine and Community Health.2023; 11(3): e002271. CrossRef - Social isolation, loneliness and subsequent risk of major adverse cardiovascular events among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yannis Yan Liang, Yilin Chen, Hongliang Feng, Huachen Xue, Yu Nie, Qi-Yong H Ai, Jiacheng Ma, Lulu Yang, Jihui Zhang, Sizhi Ai
General Psychiatry.2023; 36(6): e101153. CrossRef - Stress, Depression, and Unhealthy Behavior Changes among Patients with Diabetes during COVID-19 in Korea
Hae Ran Kim, Jeong-Soon Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 303. CrossRef - Reply to comment on “Unexpected decline in glycated hemoglobin level after emergency COVID‐19 measures in three robust older Japanese women with prediabetes/mild type 2 diabetes”
Tazuo Okuno, Osamu Iritani, Kumie Kodera, Daisuke Hama, Asami Kane, Kozue Morigaki, Toshio Terai, Norie Maeno, Shigeto Morimoto
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2022; 22(7): 541. CrossRef - Anxiety, Distress and Stress among Patients with Diabetes during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Rubén A. García-Lara, José L. Gómez-Urquiza, María José Membrive-Jiménez, Almudena Velando-Soriano, Monserrat E. Granados-Bolivar, José L. Romero-Béjar, Nora Suleiman-Martos
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(9): 1412. CrossRef - Prevalence of Depression and Related Factors among Patients with Chronic Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Rubén A. García-Lara, Nora Suleiman-Martos, María J. Membrive-Jiménez, Victoria García-Morales, Miguel Quesada-Caballero, Isabel M. Guisado-Requena, José L. Gómez-Urquiza
Diagnostics.2022; 12(12): 3094. CrossRef
- Preliminary efficacy of a technology-based physical activity intervention for older Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Cardiovascular Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors Compared to DPP4 Inhibitors and Sulfonylureas as the Second-Line of Therapy in T2DM Using Large, Real-World Clinical Data in Korea
- Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):502-504. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0158
- 3,399 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals in traumatic brain injury: mechanistic insights and pharmacological implications
Gulam Mustafa Hasan, Saleha Anwar, Anas Shamsi, Sukhwinder Singh Sohal, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals in traumatic brain injury: mechanistic insights and pharmacological implications
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
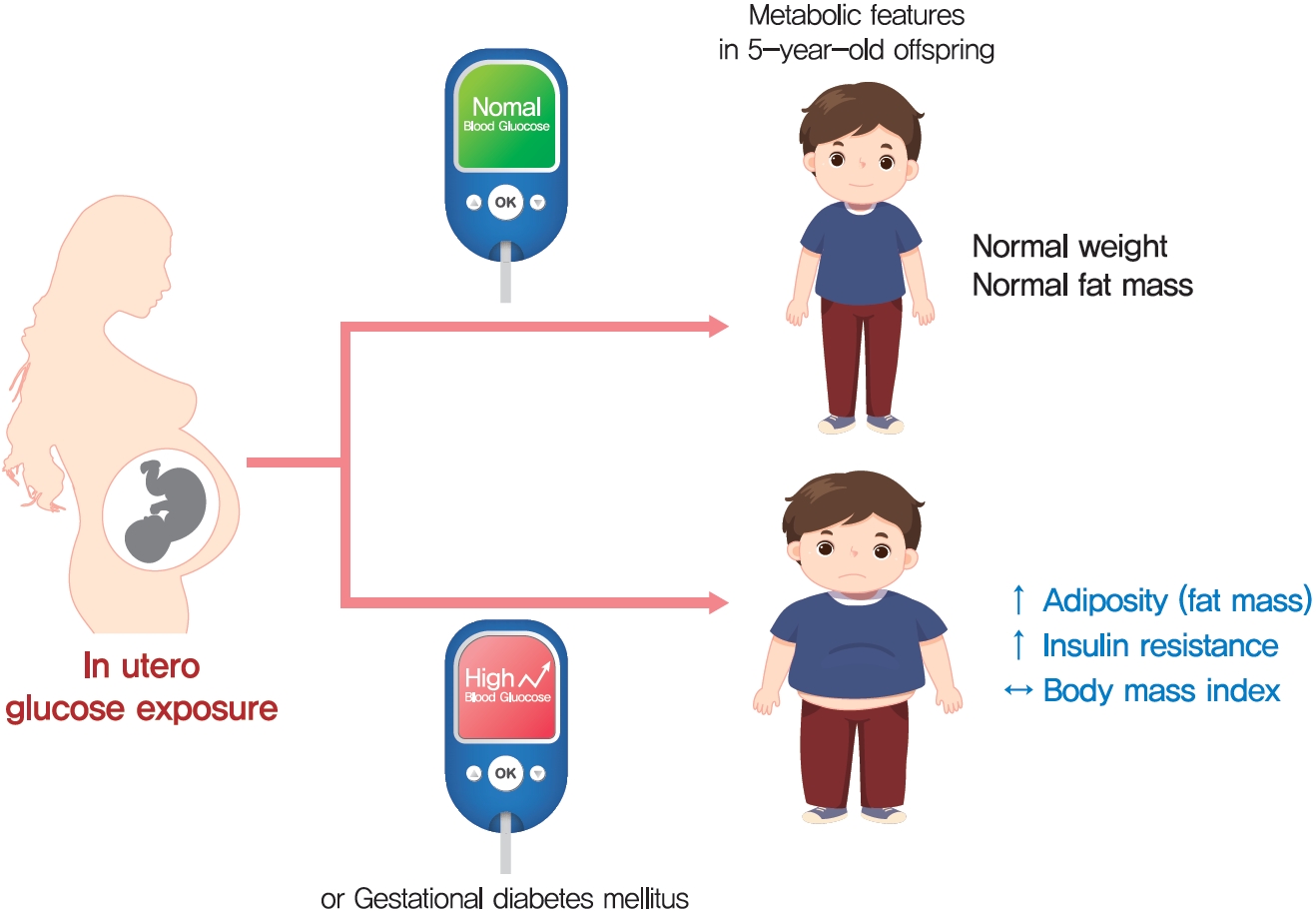
- Maternal Hyperglycemia during Pregnancy Increases Adiposity of Offspring
- Hye Rim Chung, Joon Ho Moon, Jung Sub Lim, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Joon-Seok Hong, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):730-738. Published online February 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0154
- 5,723 View
- 180 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
The effect of intrauterine hyperglycemia on fat mass and regional fat proportion of the offspring of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus (OGDM) remains to be determined.
Methods
The body composition of OGDM (n=25) and offspring of normoglycemic mothers (n=49) was compared using dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry at age 5 years. The relationship between maternal glucose concentration during a 100 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and regional fat mass or proportion was analyzed after adjusting for maternal prepregnancy body mass index (BMI).
Results
BMI was comparable between OGDM and control (median, 16.0 kg/m2 vs. 16.1 kg/m2 ). Total, truncal, and leg fat mass were higher in OGDM compared with control (3,769 g vs. 2,245 g, P=0.004; 1,289 g vs. 870 g, P=0.017; 1,638 g vs. 961 g, P=0.002, respectively), whereas total lean mass was lower in OGDM (15,688 g vs. 16,941 g, P=0.001). Among OGDM, total and truncal fat mass were correlated with fasting and 3-hour glucose concentrations of maternal 100 g OGTT during pregnancy (total fat mass, r=0.49, P=0.018 [fasting], r=0.473, P=0.023 [3-hour]; truncal fat mass, r=0.571, P=0.004 [fasting], r=0.558, P=0.006 [3-hour]), but there was no correlation between OGDM leg fat mass and maternal OGTT during pregnancy. Regional fat indices were not correlated with concurrent maternal 75 g OGTT values.
Conclusion
Intrauterine hyperglycemia is associated with increased fat mass, especially truncal fat, in OGDM aged 5 years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in free fatty acid profiles in gestational diabetes mellitus
Haoyi Du, Danyang Li, Laura Monjowa Molive, Na Wu
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - High-fat diet during pregnancy lowers fetal weight and has a long-lasting adverse effect on brown adipose tissue in the offspring
Mihoko Yamaguchi, Jun Mori, Nozomi Nishida, Satoshi Miyagaki, Yasuhiro Kawabe, Takeshi Ota, Hidechika Morimoto, Yusuke Tsuma, Shota Fukuhara, Takehiro Ogata, Takuro Okamaura, Naoko Nakanishi, Masahide Hamaguchi, Hisakazu Nakajima, Michiaki Fukui, Tomoko I
Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease.2023; 14(2): 261. CrossRef - Prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus in Asian women using machine learning algorithms
Byung Soo Kang, Seon Ui Lee, Subeen Hong, Sae Kyung Choi, Jae Eun Shin, Jeong Ha Wie, Yun Sung Jo, Yeon Hee Kim, Kicheol Kil, Yoo Hyun Chung, Kyunghoon Jung, Hanul Hong, In Yang Park, Hyun Sun Ko
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Increased Pro-Inflammatory T Cells, Senescent T Cells, and Immune-Check Point Molecules in the Placentas of Patients With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Min-Kyung Yeo, Jung Tae Kim, Danbit Park, Yewon Jung, Ok Soon Kim, Seong Eun Lee, Ji Min Kim, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Mina Lee, Hyun Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in free fatty acid profiles in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Response: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (
Diabetes metab J 2019;43;276-86) - Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):547-548. Published online August 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0148
- 3,486 View
- 42 Download
- 1 Crossref
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients Treated with Statins for Residual Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
- Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jae Myung Yu, Sung Rae Kim, In Kye Lee, Kyung-Ah Han, Sung Hee Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Ji-Oh Mok, Yong-ho Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, So Hun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Ah Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Sung-Ho Her, Won Yong Shin, Mi-Seung Shin, Hyo-Suk Ahn, Seung Ho Kang, Jin-Man Cho, Sang-Ho Jo, Tae-Joon Cha, Seok Yeon Kim, Kyung Heon Won, Dong-Bin Kim, Jae Hyuk Lee, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):78-90. Published online June 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0265
- 9,276 View
- 189 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Cardiovascular risk remains increased despite optimal low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level induced by intensive statin therapy. Therefore, recent guidelines recommend non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) as a secondary target for preventing cardiovascular events. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and tolerability of omega-3 fatty acids (OM3-FAs) in combination with atorvastatin compared to atorvastatin alone in patients with mixed dyslipidemia.
Methods This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, and phase III multicenter study included adults with fasting triglyceride (TG) levels ≥200 and <500 mg/dL and LDL-C levels <110 mg/dL. Eligible subjects were randomized to ATOMEGA (OM3-FAs 4,000 mg plus atorvastatin calcium 20 mg) or atorvastatin 20 mg plus placebo groups. The primary efficacy endpoints were the percent changes in TG and non-HDL-C levels from baseline at the end of treatment.
Results After 8 weeks of treatment, the percent changes from baseline in TG (−29.8% vs. 3.6%,
P <0.001) and non-HDL-C (−10.1% vs. 4.9%,P <0.001) levels were significantly greater in the ATOMEGA group (n =97) than in the atorvastatin group (n =103). Moreover, the proportion of total subjects reaching TG target of <200 mg/dL in the ATOMEGA group was significantly higher than that in the atorvastatin group (62.9% vs. 22.3%,P <0.001). The incidence of adverse events did not differ between the two groups.Conclusion The addition of OM3-FAs to atorvastatin improved TG and non-HDL-C levels to a significant extent compared to atorvastatin alone in subjects with residual hypertriglyceridemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between Omega‐3 Fatty Acid Intake and Dyslipidemia: A Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Tianjiao Wang, Xin Zhang, Na Zhou, Yuxuan Shen, Biao Li, Bingshu E. Chen, Xinzhi Li
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutraceutical support in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
E. V. Gracheva, E. A. Starovoytova, E. S. Kulikov, N. A. Kirillova, S. V. Fedosenko, M. A. Balaganskaya, D. V. Kromka
Rational Pharmacotherapy in Cardiology.2023; 19(3): 298. CrossRef - Effect of coadministration of omega-3 fatty acids with glimepiride on glycemic control, lipid profile, irisin, and sirtuin-1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized controlled trial
Rehab H. Werida, Aalaa Ramzy, Youssri Nassief Ebrahim, Maged Wasfy Helmy
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Dietary Interventions on Hypertriglyceridemia: From Public Health to Molecular Nutrition Evidence
Karla Paulina Luna-Castillo, Xochitl Citlalli Olivares-Ochoa, Rocío Guadalupe Hernández-Ruiz, Iris Monserrat Llamas-Covarrubias, Saraí Citlalic Rodríguez-Reyes, Alejandra Betancourt-Núñez, Barbara Vizmanos, Erika Martínez-López, José Francisco Muñoz-Valle
Nutrients.2022; 14(5): 1104. CrossRef - The effect of omega-3 fatty acids and its combination with statins on lipid profile in patients with hypertriglyceridemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yunjiao Yang, Wen Deng, Yanmei Wang, Tongyi Li, Yiding Chen, Cong Long, Qing Wen, Yue Wu, Qiu Chen
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Atorvastatin 40 mg/ω-3 Fatty Acids 4 g Fixed-dose Combination and Atorvastatin 40 mg Monotherapy in Hypertriglyceridemic Patients who Poorly Respond to Atorvastatin 40 mg Monotherapy: An 8-week, Multicenter, Random
Jong Shin Woo, Soon Jun Hong, Dong Hoon Cha, Kee Sik Kim, Moo Hyun Kim, Jun-Won Lee, Myung Ho Jeong, Jin-Ok Jeong, Jun-Hee Lee, Doo Soo Jeon, Eun Joo Cho, Soon Kil Kim, Jun Kwan, Chang Gyu Park, Hae Young Lee, Taek Jong Hong, Jinho Shin, Ho Joong Youn, Do
Clinical Therapeutics.2021; 43(8): 1419. CrossRef - All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Death between Statins and Omega-3 Supplementation: A Meta-Analysis and Network Meta-Analysis from 55 Randomized Controlled Trials
Jeongseon Kim, Tung Hoang, Ji-Myung Kim, So Young Bu, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Eunju Park, Seung-Min Lee, Eunmi Park, Ji Yeon Min, In Seok Lee, So Young Youn, Jee-Young Yeon
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 3203. CrossRef
- Association Between Omega‐3 Fatty Acid Intake and Dyslipidemia: A Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Clinical Care/Education
- Pregnancy Outcomes of Women Additionally Diagnosed as Gestational Diabetes by the International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Criteria
- Min Hyoung Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung-Hoon Kim, Joon Seok Hong, Hye Rim Chung, Sung Hee Choi, Moon Young Kim, Hak C. Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):766-775. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0192
- 5,966 View
- 89 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the pregnancy outcomes in women who were diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) by the International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) criteria but not by the Carpenter-Coustan (CC) criteria.
Methods A total of 8,735 Korean pregnant women were identified at two hospitals between 2014 and 2016. Among them, 2,038 women participated in the prospective cohort to investigate pregnancy outcomes. Diagnosis of GDM was made via two-step approach with 50-g glucose challenge test for screening followed by diagnostic 2-hour 75-g oral glucose tolerance test. Women were divided into three groups: non-GDM, GDM diagnosed exclusively by the IADPSG criteria, and GDM diagnosed by the CC criteria.
Results The incidence of GDM was 2.1% according to the CC criteria, and 4.1% by the IADPSG criteria. Women diagnosed with GDM by the IADPSG criteria had a higher body mass index (22.0±3.1 kg/m2 vs. 21.0±2.8 kg/m2,
P <0.001) and an increased risk of preeclampsia (odds ratio [OR], 6.90; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.84 to 25.87;P =0.004) compared to non-GDM women. Compared to neonates of the non-GDM group, those of the IADPSG GDM group had an increased risk of being large for gestational age (OR, 2.39; 95% CI, 1.50 to 3.81;P <0.001), macrosomia (OR, 2.53; 95% CI, 1.26 to 5.10;P =0.009), and neonatal hypoglycemia (OR, 3.84; 95% CI, 1.01 to 14.74;P =0.049); they were also at an increased risk of requiring phototherapy (OR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.07 to 2.31;P =0.022) compared to the non-GDM group.Conclusion The IADPSG criteria increased the incidence of GDM by nearly three-fold, and women diagnosed with GDM by the IADPSG criteria had an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes in twin and singleton pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Elena Greco, Maria Calanducci, Kypros H. Nicolaides, Eleanor V.H. Barry, Mohammed S.B. Huda, Stamatina Iliodromiti
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2024; 230(2): 213. CrossRef - Neonatal outcomes according to different glucose threshold values in gestational diabetes: a register-based study
Kaisa Kariniemi, Marja Vääräsmäki, Tuija Männistö, Sanna Mustaniemi, Eero Kajantie, Sanna Eteläinen, Elina Keikkala, Anneli Pouta, Risto Kaaja, Johan G Eriksson, Hannele Laivuori, Mika Gissler
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pregnancy complications in women with pregestational and gestational diabetes mellitus
Lukas Reitzle, Christin Heidemann, Jens Baumert, Matthias Kaltheuner, Heinke Adamczewski, Andrea Icks, Christa Scheidt-Nave
Deutsches Ärzteblatt international.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Treatment of women with mild gestational diabetes mellitus decreases the risk of adverse perinatal outcomes
Fanny Goyette, Bi Lan Wo, Marie-Hélène Iglesias, Evelyne Rey, Ariane Godbout
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101458. CrossRef - Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test
Mohammadali Shahriari, Ali Shahriari, Maryam Khooshideh, Anahita Dehghaninezhad, Arezoo Maleki-Hajiagha, Rana Karimi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(2): 1347. CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus
Tae Jung Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 414. CrossRef - Update on gestational diabetes and adverse pregnancy outcomes
Bryan Ugwudike, ManHo Kwok
Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology.2023; 35(5): 453. CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Can Triglyceride/Glucose Index (TyG) and Triglyceride/HDL-Cholesterol Ratio (TG/HDL-c) Predict Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
Seval YILMAZ ERGANİ, Tolgay Tuyan İLHAN, Betül TOKGÖZ, Burak BAYRAKTAR, Mevlüt BUCAK, Müjde Can İBANOĞLU, Kadriye YAKUT YÜCEL, Kadriye ERDOĞAN, Cantekin İSKENDER, Yaprak ÜSTÜN
Ankara Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi Tıp Dergisi.2023; 56(2): 117. CrossRef - Risk factors for postpartum urinary incontinence: The impact of early-onset and late-onset Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a nested case-control study
Carlos I. Sartorão Filho, Fabiane A. Pinheiro, Luiz Takano, Caroline B. Prudêncio, Sthefanie K. Nunes, Hallur RLS, Iracema M.P. Calderon, Angélica M.P. Barbosa, Marilza V.C. Rudge
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2023; 290: 5. CrossRef - Review of the Screening Guidelines for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: How to Choose Wisely
Ravleen Kaur Bakshi, Akshay Kumar, Vandana Gupta, A.G. Radhika, Puneet Misra, Pankaj Bhardwaj
Indian Journal of Community Medicine.2023; 48(6): 828. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Risk and Risk Factors for Postpartum Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Mi Jin Choi, Jimi Choi, Chae Weon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 112. CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus: current screening problems
N. I. Volkova, S. O. Panenko
Diabetes mellitus.2022; 25(1): 72. CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis
Wenrui Ye, Cong Luo, Jing Huang, Chenglong Li, Zhixiong Liu, Fangkun Liu
BMJ.2022; : e067946. CrossRef - Effect of Different Types of Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Adverse Neonatal Outcomes: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Marzieh Saei Ghare Naz, Razieh Bidhendi-Yarandi, Samira Behboudi-Gandevani
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 605. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Jung A Kim, Jinsil Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108533. CrossRef - Effect of the IADPSG screening strategy for gestational diabetes on perinatal outcomes in Switzerland
Evelyne M. Aubry, Luigi Raio, Stephan Oelhafen
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108830. CrossRef - Estimated impact of introduction of new diagnostic criteria for gestational diabetes mellitus
Leon de Wit, Anna B Zijlmans, Doortje Rademaker, Christiana A Naaktgeboren, J Hans DeVries, Arie Franx, Rebecca C Painter, Bas B van Rijn
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(6): 868. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected At 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists Until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 547. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the risk of insulin-requiring gestational diabetes
Sang Youn You, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hawn Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal Hyperglycemia during Pregnancy Increases Adiposity of Offspring
Hye Rim Chung, Joon Ho Moon, Jung Sub Lim, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Joon-Seok Hong, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 730. CrossRef - Prepregnancy smoking and the risk of gestational diabetes requiring insulin therapy
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sang Youn You, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnosis and Glycemic Control
Tae Jung Oh, Hak Chul Jang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(2): 69. CrossRef - New Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Pregnancy Outcomes in Korea
Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 763. CrossRef
- Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes in twin and singleton pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Progression to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Women with One Abnormal Value in Repeated Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests
- Sunyoung Kang, Min Hyoung Kim, Moon Young Kim, Joon-Seok Hong, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C. Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):607-614. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0159
- 5,884 View
- 103 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Women with one abnormal value (OAV) in a 100 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) during pregnancy are reported to have an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. However, there is limited data about whether women with OAV will progress to gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) when the OGTT is repeated.
Methods To identify clinical and metabolic predictors for GDM in women with OAV, we conducted a retrospective study and identified women with OAV in the OGTT done at 24 to 30 weeks gestational age (GA) and repeated the second OGTT between 32 and 34 weeks of GA.
Results Among 137 women with OAV in the initial OGTT, 58 (42.3%) had normal, 40 (29.2%) had OAV and 39 (28.5%) had GDM in the second OGTT. Maternal age, prepregnancy body mass index, weight gain from prepregnancy to the second OGTT, GA at the time of the OGTT, and parity were similar among normal, OAV, and GDM groups. Plasma glucose levels in screening tests were different (151.8±15.7, 155.8±14.6, 162.5±20.3 mg/dL,
P <0.05), but fasting, 1-, 2-, and 3-hour glucose levels in the initial OGTT were not. Compared to women with screen negative, women with untreated OAV had a higher frequency of macrosomia.Conclusion We demonstrated that women with OAV in the initial OGTT significantly progressed to GDM in the second OGTT. Clinical parameters predicting progression to GDM were not found. Repeating the OGTT in women with OAV in the initial test may be helpful to detect GDM progression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test
Mohammadali Shahriari, Ali Shahriari, Maryam Khooshideh, Anahita Dehghaninezhad, Arezoo Maleki-Hajiagha, Rana Karimi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(2): 1347. CrossRef - One abnormal value or vomiting after oral glucose tolerance test in pregnancy: incidence and impact on maternal-fetal outcomes
Humberto Navarro-Martinez, Juana-Antonia Flores-Le Roux, Gemma Llauradó, Lucia Gortazar, Antonio Payà, Laura Mañé, Juan Pedro-Botet, David Benaiges
Gynecological Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the gut microflora in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Xuping Wang, Bingfeng Bian, Fuman Du, Chaofeng Xiang, Yu Liu, Na Li, Binhong Duan
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between gestational impaired glucose tolerance and hyperglycemic markers: A prospective study
Ohad Gluck, Hadas Ganer Herman, Nataly Fainstein, Neri Katz, Jacob Bar, Michal Kovo
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2022; 156(1): 82. CrossRef - Association of abnormal-glucose tolerance during pregnancy with exposure to PM2.5 components and sources
Dejian Mai, Chengfang Xu, Weiwei Lin, Dingli Yue, Shaojie Fu, Jianqing Lin, Luan Yuan, Yan Zhao, Yuhong Zhai, Huiying Mai, Xiaoling Zeng, Tingwu Jiang, Xuejiao Li, Jiajia Dai, Boning You, Qin Xiao, Qing Wei, Qiansheng Hu
Environmental Pollution.2022; 292: 118468. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnosis and Glycemic Control
Tae Jung Oh, Hak Chul Jang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(2): 69. CrossRef - Health literacy and diabetes control in pregnant women
Azar Pirdehghan, Mohammad Eslahchi, Farzaneh Esna-Ashari, Shiva Borzouei
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(2): 1048. CrossRef
- Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





